Pinned Post
where is biomass energy used the most
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Exploring Biomass Resources for Renewable Energy
1. What are biomass resources and their significance for renewable energy?
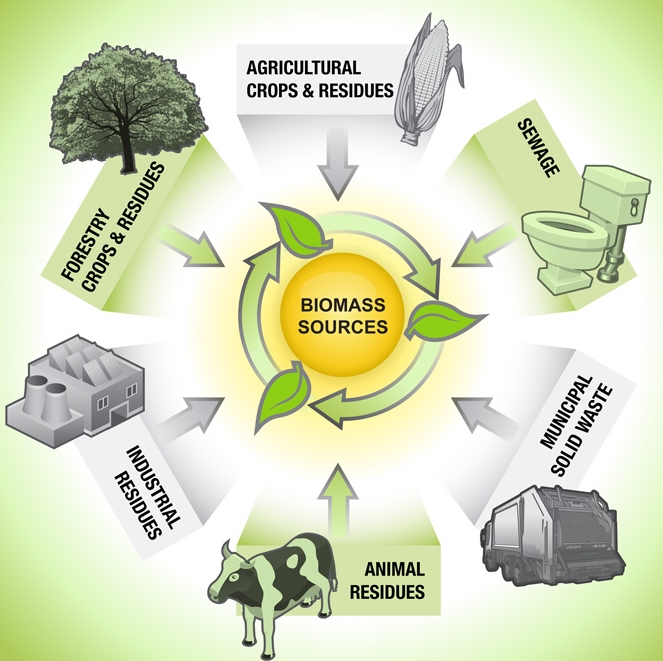
Biomass resources refer to organic matter derived from plants, animals, and their by-products that can be utilized to produce renewable energy. These resources include agricultural residues, forest residues, dedicated energy crops, and organic wastes such as food and yard waste.
Significance:
- Biomass resources are considered a renewable energy source as they can be replenished within a human lifespan.
- They offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
- Biomass resources can contribute to rural development by creating employment opportunities and promoting economic growth in agricultural communities.
2. How is biomass transformed into renewable energy?
Biomass can be converted into renewable energy through various processes:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used directly for heating or converted into electricity through steam turbines.
- Gasification: Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce a gas called syngas, which can be used for electricity generation or as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and fuels.
- Anaerobic digestion: Microorganisms break down biomass in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide) that can be used for cooking, heating, or electricity generation.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen to produce bio-oil, syngas, and char. These can be further processed into liquid fuels or used as precursors for the chemical industry.
3. What are the benefits of using biomass for renewable energy?

The utilization of biomass for renewable energy offers several benefits:
- Reduces carbon emissions: Biomass energy has a neutral carbon footprint as the carbon released during its combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during plant growth. This helps to mitigate climate change and reduce global warming.
- Waste management: Biomass resources provide an opportunity to divert organic waste from landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the generation of harmful pollutants.
- Energy security: Biomass reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, promoting energy self-sufficiency and reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations.
- Job creation: The biomass industry creates employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas where agricultural resources are abundant.
4. Can biomass be used to generate electricity?
Yes, biomass can be used to generate electricity through various methods:
- Direct combustion: Biomass is burned in power plants to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas (syngas) that can be burned to generate electricity.
- Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by microorganisms in a digester, producing biogas that can be used in engines or turbines to generate electricity.
These processes enable the production of renewable electricity from biomass resources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a more sustainable energy mix.
5. How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass has several advantages over other renewable energy sources:
- Continuous availability: Unlike solar or wind energy, biomass resources can be stored and used as needed, providing a reliable source of energy on-demand.
- Energy-dense: Biomass has a higher energy density compared to wind or solar, making it more suitable for applications requiring high energy outputs.
- Provides baseload power: Biomass can be used to produce baseload power, which is consistent and stable, similar to the power generated by fossil fuel power plants.
However, biomass also has certain limitations, such as the need for sustainable sourcing, potential competition with food production, and the emission of air pollutants if not properly managed.
6. What are the environmental impacts of biomass energy?
The environmental impacts of biomass energy can vary depending on the specific feedstock and conversion technology used. However, some common environmental considerations include:
- Greenhouse gas emissions: While biomass combustion is carbon-neutral in theory, improper combustion or the use of unsustainable feedstocks may result in the release of greenhouse gases and pollutants.
- Land use change: Expanding the cultivation of energy crops may lead to deforestation or the conversion of valuable natural ecosystems, which can have negative ecological effects.
- Biodiversity loss: Inappropriate land management practices associated with biomass production may result in habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity.
- Water usage: Certain biomass conversion processes, such as biofuel production, require significant water inputs, which can strain local water resources if not properly managed.
To minimize these impacts, sustainable sourcing, efficient conversion technologies, and proper environmental management strategies are essential.
7. Are there any financial incentives for using biomass for renewable energy?
In many countries, there are financial incentives and support mechanisms in place to encourage the use of biomass for renewable energy:
- Feed-in tariffs: Governments may provide guaranteed payment rates for electricity generated from biomass, ensuring a stable income stream for biomass power producers.
- Tax incentives: Tax credits or exemptions can be offered to biomass energy producers, reducing the overall costs of installation and operation.
- Grants and subsidies: Governments and organizations may offer grants or subsidies to support the development of biomass projects and research initiatives.
These financial incentives aim to incentivize the adoption of biomass energy and promote its growth as a renewable energy source.
8. Can biomass energy help reduce waste management issues?
Yes, biomass energy can have a significant impact on waste management:
- Diversion of organic waste: Biomass resources, including agricultural residues, food waste, and forest residues, can be diverted from landfills and incinerators, reducing the environmental impacts associated with waste disposal.
- Generation of renewable energy: By utilizing biomass for energy production, waste materials can be transformed into valuable resources, reducing the demand for non-renewable energy sources.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: The decomposition of organic waste in landfills generates methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By diverting this waste to biomass energy production, the emissions can be significantly reduced.
Implementing effective waste management strategies that prioritize biomass utilization can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
9. Can all types of biomass be used for renewable energy?
While a wide variety of biomass resources can be used for renewable energy, not all types are equally suitable or sustainable:
- Preferred biomass resources: Agricultural residues, forest residues, dedicated energy crops, and organic wastes are considered preferred feedstocks due to their abundance and potential to be sourced sustainably.
- Unsuitable biomass types: Biomass from unsustainable or environmentally sensitive sources, such as old-growth forests or food crops meant for human consumption, should be avoided to prevent negative ecological and food security impacts.
It is crucial to assess the sustainability and environmental credentials of biomass feedstocks before utilizing them for renewable energy production.
10. Can biomass energy be used on a small scale?
Yes, biomass energy can be utilized on a small scale for various applications:
- Residential heating: Biomass boilers or stoves can be used to provide heat for individual homes or small communities.
- Cooking and heating in rural areas: In off-grid or rural areas, biomass energy can be used for cooking, heating, and lighting, providing reliable and sustainable energy access.
- Community-scale power generation: Biomass power plants can be designed to meet the electricity needs of small towns or communities, offering a decentralized and sustainable energy solution.
The scalability of biomass energy makes it adaptable to different settings, from individual households to larger communities.
11. Is biomass energy a cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels?
Biomass energy can be cost-effective compared to fossil fuels under certain conditions:
- Feedstock availability: Biomass resources should be locally available and affordable to minimize transportation costs.
- Technological efficiency: Efficient conversion technologies and well-designed equipment contribute to lowering the overall costs of biomass energy production.
- Government support: Financial incentives, grants, and supportive policies can help reduce the upfront costs and improve the competitiveness of biomass energy.
However, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, considering factors such as feedstock availability, processing costs, and the potential for revenue generation through the sale of by-products.
12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future outlook for biomass energy is promising, with several factors driving its growth:
- Renewable energy targets: Many countries have established renewable energy targets, and biomass is expected to play a significant role in achieving these goals.
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development efforts are improving biomass conversion technologies, increasing efficiency, and reducing costs.
- Sustainable sourcing practices: The adoption of sustainable biomass production and sourcing practices will ensure the long-term viability and environmental benefits of biomass energy.
- Integration with other sectors: Biomass energy can be integrated with other sectors, such as agriculture and forestry, creating synergies and promoting sustainable land management.
As the world transitions towards a low-carbon economy, biomass energy will continue to evolve and contribute to the global energy mix.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment